Mild Hybrid Cars
What is a Mild Hybrid Car?
Green Basics Advanced Green Steps Speaking Green Success Stories

Green Basics Advanced Green Steps Speaking Green Success Stories
|
Home > Advanced Green Steps > Green Cars > Mild Hybrid Cars |
Hybrid cars use a combination of an electric motor and a traditional gasoline engine to power the vehicle. There are three types of hybrid cars; Mild Hybrid, Full Hybrid, and Plug-In Hybrid.
Mild hybrid cars are the least fuel efficient of the three types of hybrids. There are a few different ways they can save on fuel, depending on the design. Some turn off the engine when stopped, to prevent the engine from idling and instantly start when the gas pedal is pressed again. Another way they may save fuel is to use the electric motor to assist the gas engine.
The mileage for mild hybrids are not significantly improved over non-hybrid cars. Starting in 2010, GM has stopped producing cars such as the Chevy Malibu Hybrid. Here are some examples of mid-sized cars to compare the mileage of Mild Hybrid Cars, Full Hybrid Cars, and traditional cars: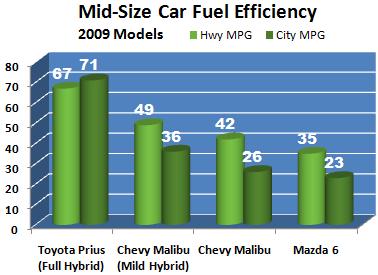
see government fuel consumption ratings for ratings on all vehicles.
The Chevy Malibu Hybrid and Saturn Aura Hybrid are two examples of mild hybrids. Another example of a mild hybrid is the Chevy Siverado Hybrid.
The batteries in hybrids need to get recharged. This can be done in several ways. The first is to use regenerative breaking. When slowing down, or stopping a car, the momentum of the car is slowed down using break pads. Regenerative breaks capture the energy (kinetic energy) that is normally lost when breaking. This energy is then transferred to the batteries that run the electric motor
Another way the batteries get recharges are from the gas engine during normal driving. When the engine is not in high demand, the additional energy will be captured in the batteries. A good example of this is when the car is travelling down a steep hill, the engine transfers its power to the batteries while it is not being used to move the vehicle.